As of 1.1.2023, maximum levels for PFAS in certain foodstuffs of animal origin will apply. AGROLAB LUFA GmbH has expanded its range of tests to include the accredited determination of perfluorinated and polyfluorinated alkyl substances.
In EU Regulation 2022/2388 of Dec. 7, 2022, binding limits are set for the four most important representatives of PFAS for certain foods of animal origin. These are the following compounds:
|
Regulated perfluoro alkyl substances |
|
|
PFOS |
Perfluorooctane sulfonic acid |
|
PFOA |
Perfluorooctanoic acid |
|
PFNA |
Perfluorononanoic acid |
|
PFHxS |
Perfluorohexanesulfonic acid |
These substances are examples of thousands of perfluorinated and polyfluorinated alkyl substances that have been used in many industrial applications for decades and whose residues are now distributed ubiquitously in the environment. All compounds have in common that they are difficult to biodegrade and are therefore described as persistent. They enter our food through bioaccumulation within food chains, but also through packaging and contact materials.
It has now been scientifically proven that accumulation of the compounds in the human and animal organism can also lead to adverse health effects. Liver diseases and negative influences on the immune system are particularly critical. Especially in young children, exposure can lead to the weekly tolerable intake (TWI) of 4.4 ng/kg body weight being exceeded.
On this basis, the EU Commission derived the following maximum permissible levels, which were added to the Annex of Regulation (EC) No. 1881/2006 (Contaminants Regulation):
|
Foodstuffs (1) |
PFOS* |
PFOA* |
PFNA* |
PFHxS* |
Sum ** |
|
|
10.1 |
Eggs |
1,0 |
0,30 |
0,70 |
0,30 |
1,7 |
|
10.2 |
Fishery products (26) and bivalve molluscs (26) |
|||||
|
10.2.1 |
Fish meat (24) (25) |
|||||
|
10.2.1.1 |
Muscle meat of fish, except those listed under 10.2.1.2 and 10.2.1.3 |
2,0 |
0,20 |
0,50 |
0,20 |
2,0 |
|
10.2.1.2 |
Muscle meat of the following fish, in case they are not intended for the production of food for infants and young children: Baltic herring (Clupea harengus membras) Bonito (Sarda- and Orcynopsis species) Burbot (Lota lota) European sprat (Sprattus sprattus) Flounder (Platichthys flesus and Glyptocephalus cynoglossus) Grey mullet (Mugil cephalus) Horse mackerel (Trachurus trachurus) Pike (Esox species) Plaice (Pleuronectes- and Lepidopsetta species) Sardine and pilchard (Sardina species) Seabass (Dicentrarchus species) Sea catfish (Silurus- and Pangasius species) Sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) Tench (Tinca tinca) Vendace (Coregonus albula and Coregonus vandesius) Silverly lightfish (Phosichthys argenteus) Wild salmon and wild trout (wild Salmo and Oncorhynchus species) |
7,0 |
1,0 |
2,5 |
0,2 |
8,0 |
|
10.2.1.3 |
Muscle meat of the following fish, Anchovy (Engraulis species) Babel (Barbus barbus) Bream (Abramis species) Char (Salvelinus species) Eel (Anguilla species) Pike-perch (Sander species) Perch (Perca fluviatilis) Roach (Rutilus rutilus) Smelt (Osmerus species) Whitefish (Coregonus species) |
35 |
8,0 |
8,0 |
1,5 |
45 |
|
10.2.2 |
Crustaceans (26) (47) and bivalve molluscs (26) For crustaceans the maximum level shall apply to muscle meat from appendages and abdomen 44. In case of crabs and crab-like crustaceans (Brachyura and Anomura) muscle meat from appendages. |
3,0 |
0,70 |
1,0 |
1,5 |
5,0 |
|
10.3 |
Meat and edible offal (6) |
|||||
|
10.3.1 |
Meat of bovine animals, pig and poultry |
0,3 |
0,80 |
0,20 |
0,20 |
1,3 |
|
10.3.2 |
Meat of sheep |
1,0 |
0,20 |
0,20 |
0,20 |
1,6 |
|
10.3.3 |
Offal of bovine animals, sheep, pig and poultry |
6,0 |
0,70 |
0,40 |
0,50 |
8,0 |
|
10.3.4 |
Meat of game animals, with the exception of bear meat |
5,0 |
3,5 |
1,5 |
0,60 |
9,0 |
|
10.3.5 |
Offal of game animals, with the exception of bear offal |
50 |
25 |
45 |
3,0 |
50 |
All figures in µg/kg fresh weight
* The maximum level applies to the sum of linear and branched stereoisomers, whether they are chromatographically separated or not.
** For the sum of PFOS, PFOA, PFNA and PFHxS, lower bound concentrations are calculated on the assumption that all the values below the limit of quantification are zero.
For an explanation of the footnotes, please refer to the text of the regulation.
Important: For the analysis and subsequent correct evaluation of results, it is essential that a correct species declaration is available for fish meat and that the intended use of the goods is known.
YOUR PLUS: Our LC MS/MS method is accredited for all mentioned matrices. The limit of quantification is 0.1 µg/kg for the regulated compounds, enabling legally compliant evaluation. In addition, we are also accredited to test fish oils for PFAS with a limit of quantification of 0.25 µg/kg.
Author: Dr. Frank Mörsberger

 LinkedIn
LinkedIn ALOOSTA
ALOOSTA Contact
Contact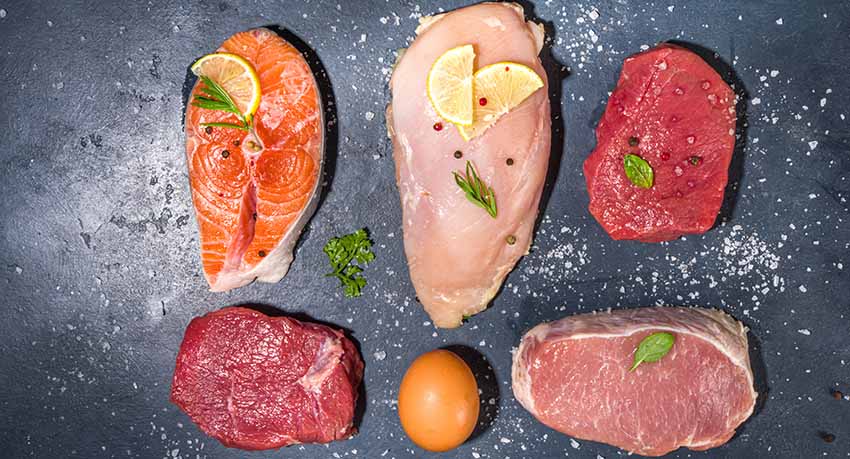
 Contact
Contact Career
Career